What’s the Difference Between Authorization Objects P_ORGIN and P_ORGXX?
What’s the Difference Between Authorization Objects P_ORGIN and P_ORGXX?
Background
The core question is quite simple:
Why do we need the P_ORGXX authorization object if P_ORGIN already exists?
Resolution
See: Authorizations for Human Resources
Let’s start with a bit of background on each of the mentioned authorization objects.
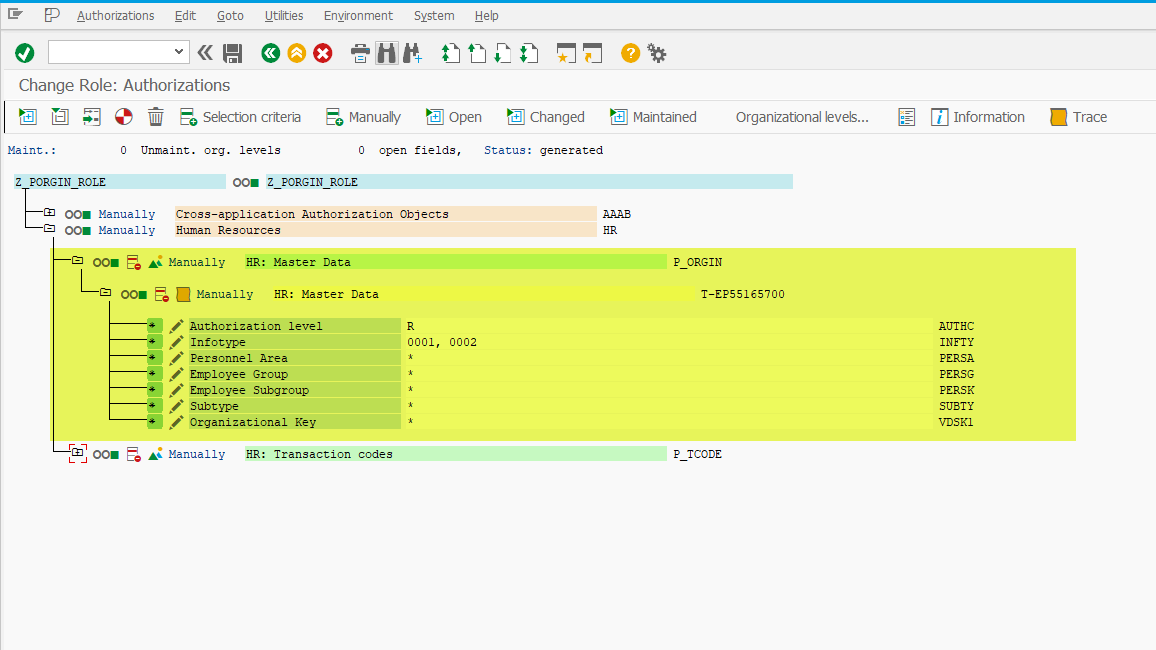
Authorization Object: P_ORGIN
See: P_ORGIN (HR: Master Data)
Definition
Authorization object that is used during the authorization check for HR infotypes. The check takes place when HR infotypes are edited or read.
P_ORGIN is one of the primary authorization objects in the HCM component, used when working with Personnel Administration infotypes. It helps define access levels to one or more infotypes. When creating custom roles, functional consultants most often work with this object.
Authorization Object: P_ORGXX
See: P_ORGXX (HR: Master Data – Extended Check)
Definition
Authorization object that is used during the authorization check for HR infotypes. The check takes place when HR infotypes are edited or read.
Описание, которое можно найти в справочном материале, как вы могли заметить, идентичное с описанием объекта полномочий P_ORGIN
At first glance, the description from the documentation appears identical to that of P_ORGIN—and that's not far from the truth, with a few key differences.
Key Differences
- P_ORGXX is an extended version of the P_ORGIN authorization object.
- It allows for access control based on values in infotype 0001 – "Organizational Assignment." In other words, it enables more granular authorization checks.
- By default, P_ORGXX is disabled in the SAP system.
See: [P_ORGXX (HR: Master Data – Extended Check)]
See P_ORGXX (HR: Master Data – Extended Check)
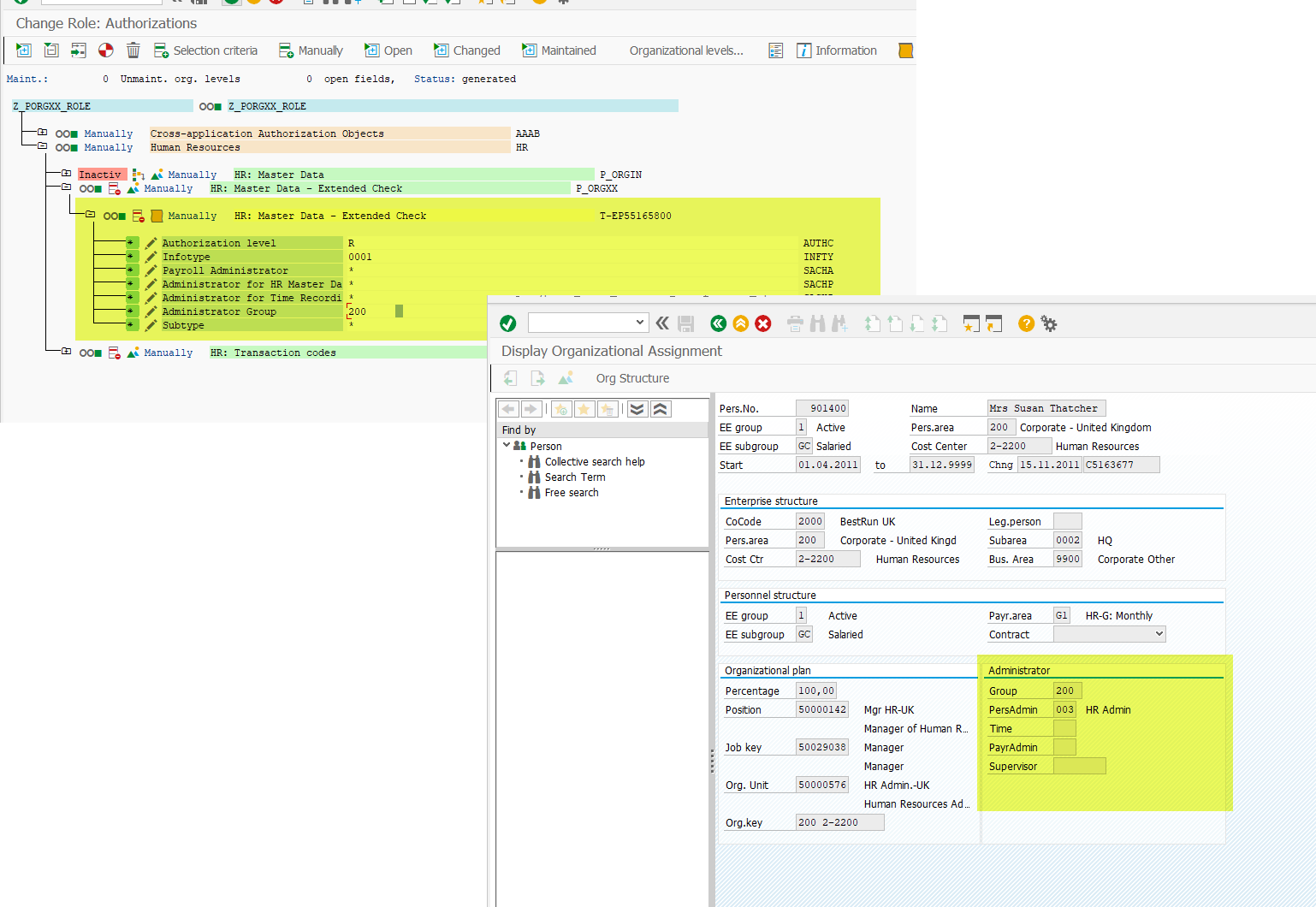
The AUTHC field contains the access mode for the authorization (for example, R = Read). See AUTHC (Authorization Level) for a detailed description of the different authorization levels possible ( M , R , S , E , D , W , * ).
The SACHA , SACHP , SACHZ , and SBMOD fields are filled from the Organizational Assignment infotype (0001). Since this infotype has time-dependent specifications, an authorization may only exist for certain time intervals depending on the user’s authorization. A user’s period of responsibility is represented by all the time intervals for which he or she has P_ORGXX authorizations
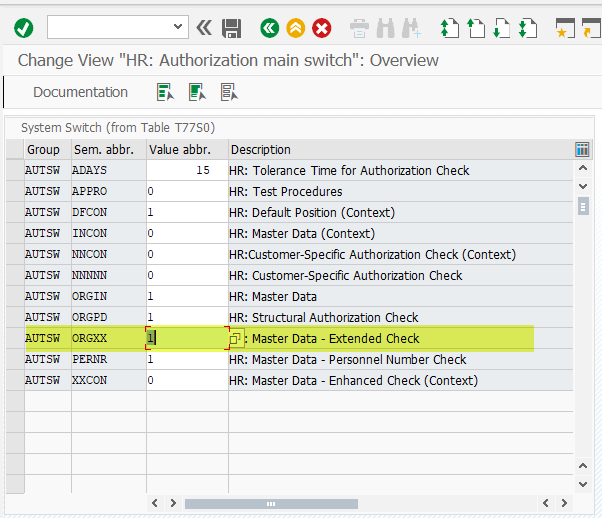
Activation
To enable or disable the use of the P_ORGXX object in an SAP system, you must change the switch AUTSW ORGXX in table T77S0
(You can also adjust this via transaction OOAC)
Note
When the switch AUTSW ORGXX is active, both P_ORGIN and P_ORGXX must be present in the user's role.
Example 1
P_ORGXX is disabled in the system. The user has read access to infotypes 0001 ("Organizational Assignment") and 0002 ("Personal Data") via transaction PA20.
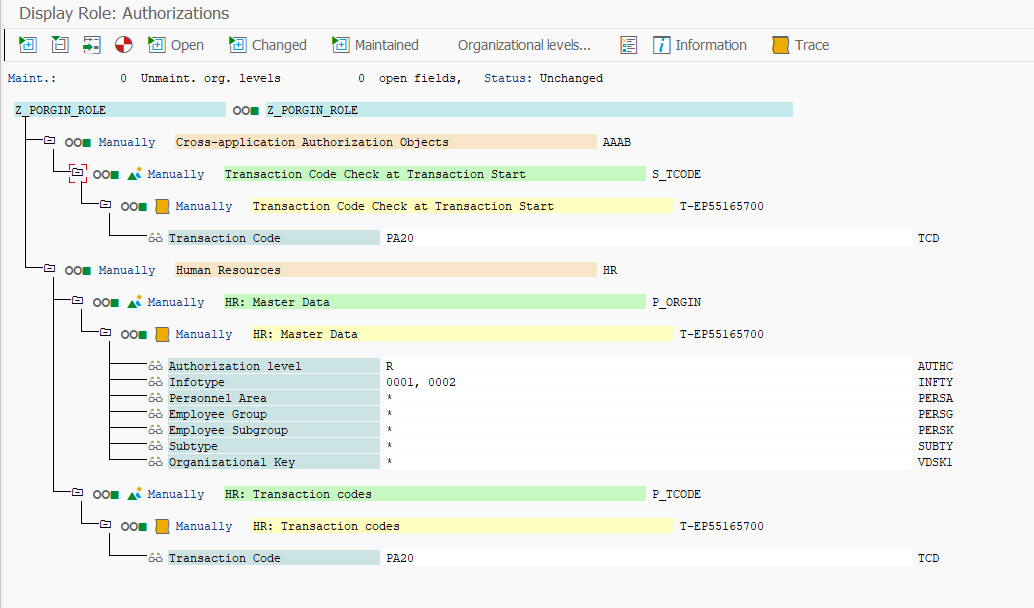
Checking:
Check successful.
Example 2
P_ORGXX is enabled in the system. The user role only includes P_ORGIN.
Result: the user cannot execute transaction PA20 because P_ORGXX is missing in their role.
Example 3
P_ORGXX is enabled in the system. The user role includes both P_ORGIN and P_ORGXX.
Result: the user can run transaction PA20, but one personnel number was skipped due to insufficient authorization.
See Tracing User Authorizations